Wave overtopping and overflow hazards: application on the Camargue sea-dike
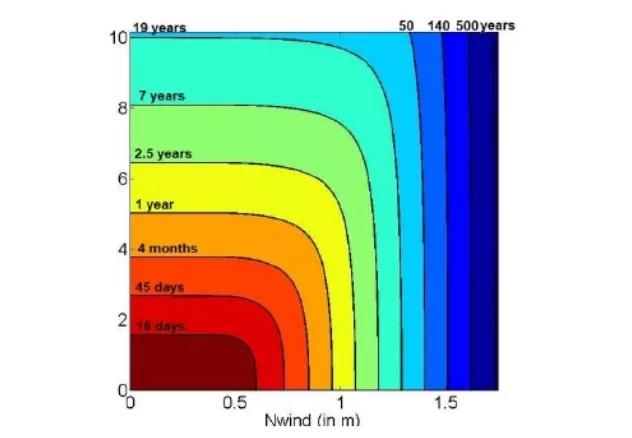
Dike breaches occurs regularly during storm events. This phenomenon contributes to amplify considerably the impact of floods on coastal areas. It represents an important cost for repairing existing infrastructures in the vicinity of the sea-dike. Then, they must be upgraded to prevent breaches. In the present study, ANEMOC and REFMAR dataset were analysed, off Camargue coasts, to quantify the storm hazards in terms of wave height and sea level wind setup. Repartition laws were adjusted on dataset to build a 2D-copula which is used to estimate events return periods. As we were interested in the physical parameters around the sea-dike, waves were propagated from the deep water by using TOMAWAC module which takes into account the actual bathymetry. As a first approximation, only a 1D propagation was considered. From estimated local parameters, overtopping formula were used to estimate the overtopping discharge, the crest velocity, and the water level over the sea-dike. These latter were used to assess a potential erosion on the dike rear-side. A set of several wave heights-sea-level wind setup couple were tested and each of them were relied to a probability of occurrence given by the 2D-copule.
T. Paul, C. Lutringer, A. Poupardin, A. Bennabi, J. Jeaong, P. Sergent
- Conf. TUC 2020, BE, Antwerp