Filtrer les publications
Update of the tsunami catalogue of New Caledonia using a decision table based on seimic data and maregraphic records
Fourteen years ago, the 26 December 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami demonstrated the destructional capability of tsunamis to the entire world. Since then, many research programs have been initiated to try to understand the phenomenon and its related hazards better and to improve the early warning systems for exposed coastal populations. Pacific Islands Countries and Territories (PICTs) are especially vulnerable to tsunamis. Amongst them, New Caledonia is a French overseas territory located in the Southwest Pacific and exposed to several tsunami sources.
J. Roger, B. Pelletier, J. Aucan
NHESS

Evaluation and combination of quad-constellation multi-GNSS multipath reflectometry applied to sea level retrieval
The satellites of the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) continuously broadcast L-band signals at about a 20-cm wavelength. Some signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) data received by off-shelf geodetic antennas contain the multipath information of the sea, and they have been demonstrated for use in retrieving sea levels; however, compared with conventional tide gauges, this GNSS multipath reflectometry (GNSS-MR) technique is limited in terms of both precision and sampling rate.
X. Wang, X. He, Q. Zhang
Remote Sensing of Environment, volume 231

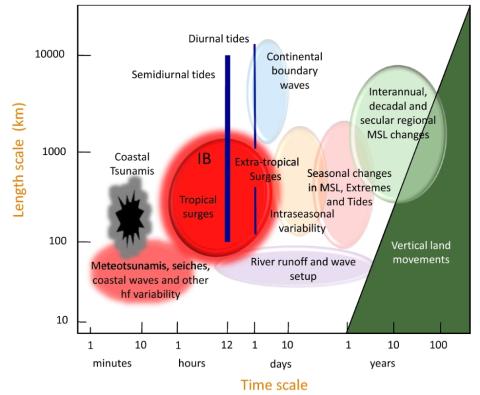
Forcing Factors Affecting Sea Level Changes at the Coast
We review the characteristics of sea level variability at the coast focussing on how it differs from the variability in the nearby deep ocean. Sea level variability occurs on all timescales, with processes at higher frequencies tending to have a larger magnitude at the coast due to resonance and other dynamics. In the case of some processes, such as the tides, the presence of the coast and the shallow waters of the shelves results in the processes being considerably more complex than offshore.
P. L. Woodworth, A. Melet, M. Marcos, R. D. Ray, G. Wöppelmann, Y. N. Sasaki, M. Cirano, A. Hibbert, J. M. Huthnance, S. Monserrat, M. A. Merrifield
Surveys in Geophysics, volume 40
Linking sea level dynamic and exceptional events to large-scale atmospheric circulation variability: A case of the Seine Bay, France
In this study, the multi-time-scale variability of the South English Channel (case of the Seine Bay, North France) sea level and its exceptional events have been investigated in relation with the global climate patterns by the use of wavelet multi-resolution decomposition techniques. The analysis has been focused on surges demodulating by an envelope approach.
I. Turki, N. Massei, B. Laignel
Oceanologia, volume 61
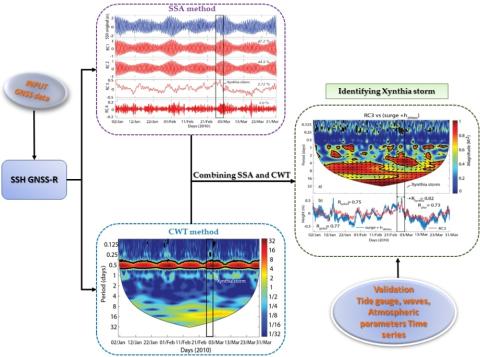
Identifying 2010 Xynthia Storm Signature in GNSS-R-Based Tide Records
In this study, three months of records (January–March 2010) that were acquired by a geodetic Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) station from the permanent network of RGP (Réseau GNSS Permanent), which was deployed by the French Geographic Institute (IGNF), located in Socoa, in the south of the Bay of Biscay, were used to determine the tide components and identify the signature of storms on the signal to noise ratio (SNR) during winter 2010.
P. Lan Vu, M. Cuong Ha, F. Frappart, J. Darrozes, G. Ramillien, G. Dufrechou, P. Gegout, D. Morichon, P. Bonneton
Remote Sensing, volume 11
New Experimental Low Cost Technique of Sea-Level Monitoring: Toward a Sea-Level Monitoring for All
In this paper, we proposed a new low cost technique of sea-level observation and monitoring inspired by the classical Tide Pole (Tide Staff). The results obtained by our proposed High Frequency Rotational Tide Gauge (RTGHF) are promising. They show that RTGHF is very adapted to an agitated environment and is able to measure high and low frequencies oscillations (waves/swells, infragravity waves, seiches, meteotsunamis, tsunamis, tides, sea-level change, etc.).
Y. Hemdane, M. Bouhmadouche, B. Hamadache, M. Aounallah
Patterns and Mechanisms of Climate, Paleoclimate and Paleoenvironmental Changes from Low-Latitude Regions, CAJG 2018, Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation, pp149-151 - Springer, Cham

Quantifying uncertainties of sandy shoreline change projections as sea level rises
Sandy shorelines are constantly evolving, threatening frequently human assets such as buildings or transport infrastructure. In these environments, sea-level rise will exacerbate coastal erosion to an amount which remains uncertain. Sandy shoreline change projections inherit the uncertainties of future mean sea-level changes, of vertical ground motions, and of other natural and anthropogenic processes affecting shoreline change variability and trends. Furthermore, the erosive impact of sea-level rise itself can be quantified using two fundamentally different models.
G. Le Cozannet, T. Bulteau, B. Castelle, R. Ranasinghe, G. Wöppelmann, J. Rohmer, N. Bernon, D. Idier, J. Louisor, D. Salas-y-Mélia
Scientific Reports, volume 9, article 42
Vertical land motion and relative sea level changes along the coastline of Brest (France) from combined space-borne geodetic methods
In spite of the recent advances and the current perspectives of satellite radar altimetry to reach the coastline and monitor coastal sea level changes, this space-borne technology remains geocentric by essence. In contrast, the quantity that matters for coastal management and society is relative sea level. That is, the sea level relative to the land, as measured by conventional tide gauges. However, two important issues are associated with the use of tide gauges.
C. Poitevin, G. Wöppelmann, D. Raucoules, G. Le Cozannet, M. Marcos, L. Testut
Remote Sensing of Environment, volume 222

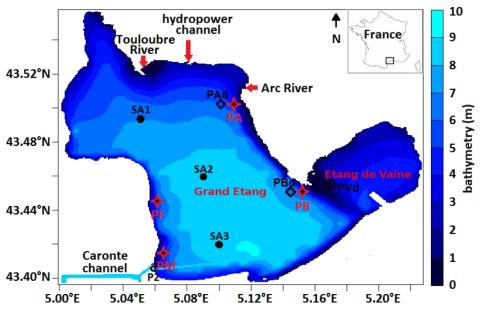
Wind effect on bottom shear stress, erosion and redeposition on Zostera noltei restoration in a coastal lagoon; part 2
This paper concerns wind effect on bottom shear stress (BSS), resuspension and redeposition of bottom sediments in the nearshore areas of the Etang de Berre (EB), a semi-enclosed lagoon, in the context of Zostera noltei (Z.n.) restoration. As in our previous paper, the first step is to compare BSS with its threshold, BSScr, for a wind speed of 21 m/s. But, here, a new simulation is performed for 16 wind directions regularly spaced. It permits to analyze the combined effect, over one year, of these winds on the erosion risk.
E. Alekseenko, B. Roux
Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, volume 216