
Filtrer les publications
Investigating the effects of sea-level rise on morphodynamics in the western Giens tombolo, France
Rising sea level along with the occurrence of greater and more frequent storms would cause not only coastal flooding, but also beach erosion and shoreline retreat problems. The Almanarre beach along the western Giens tombolo is socio-economically and heavily vulnerable to accelerated sea level rise due to its high touristic value and low-lying topography. Therefore, it is necessary to quantify the impacts of sea level rise (SLR) on the morphodynamics in this area, e.g. to evaluate the relationship between the beach erosion and SLR.
M. T. Vu, Y. Lacroix, V. T. Nguyen
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, volume 67 (ICESE 2018)
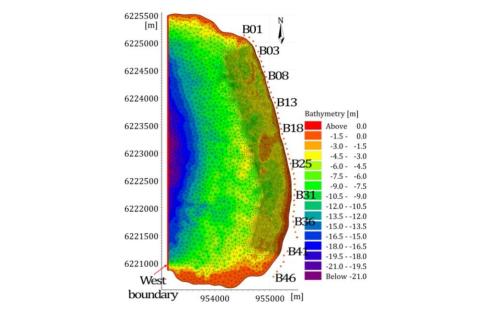
Managed realignment to mitigate storm-induced flooding: A case study in La Faute-sur-mer, France
Storm-induced coastal flooding is among the most destructive natural disasters while climate change together with increased populations along the coast will enhance the associated risk. This study presents the comparison of conventional coastal defense schemes against managed realignment schemes in La Faute-sur-Mer, a small village located in the central part of the Bay of Biscay that was severely impacted during Xynthia in 2010.
J.-R. Huguet, X. Bertin, G. Arnaud
Coastal Engineering, volume 134

Azimuth selection for sea level measurements using geodetic GPS receivers
Based on analysis of Global Positioning System (GPS) multipath signals recorded by a geodetic GPS receiver, GPS Reflectometry (GPS-R) has demonstrated unique advantages in relation to sea level monitoring. Founded on multipath reflectometry theory, sea level changes can be measured by GPS-R through spectral analysis of recorded signal-to-noise ratio data. However, prior to estimating multipath parameters, it is necessary to define azimuth and elevation angle mask to ensure the reflecting zones are on water.
X. Wang, Q. Zhang, S. Zhang
Advances in Space Research, volume 61

Tidal downscaling from the open ocean to the coast: a new approach applied to the Bay of Biscay
Downscaling physical processes from a large scale to a regional scale 3D model is a recurrent issue in coastal processes studies. The choice of boundary conditions will often greatly influence the solution within the 3D circulation model. In some regions, tides play a key role in coastal dynamics and must be accurately represented. The Bay of Biscay is one of these regions, with highly energetic tides influencing coastal circulation and river plume dynamics.
F. Toublanc, N.K. Ayouba, F. Lyarda, P. Marsaleixb, D.J. Allaina
Ocean Modelling, volume 124
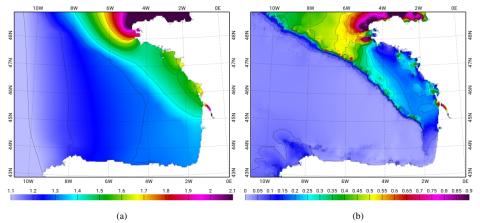
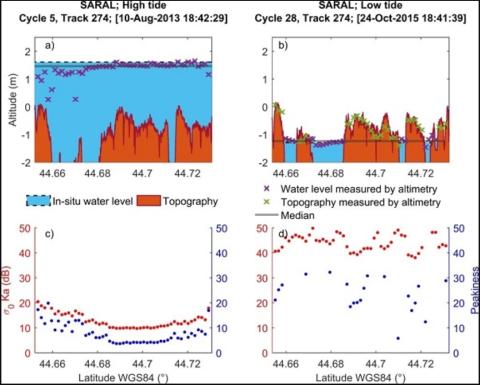
Monitoring Sea Level and Topography of Coastal Lagoons Using Satellite Radar Altimetry: The Example of the Arcachon Bay in the Bay of Biscay
Radar altimetry was initially designed to measure the marine geoid. Thanks to the improvement in the orbit determination from the meter to the centimeter level, this technique has been providing accurate measurements of the sea surface topography over the open ocean since the launch of Topex/Poseidon in 1992. In spite of a decrease in the performance over land and coastal areas, it is now commonly used over these surfaces. This study presents a semi-automatic method that allows us to discriminate between acquisitions performed at high tides and low tides.
E. Salameh, F. Frappart, V. Marieu, A. Spodar, J.-P. Parisot, V. Hanquiez, I.Turki, B. Laignel
Remote Sensing, volume 10
Coastal monitoring solutions of the geomorphological response of beach-dune systems using multi-temporal LiDAR datasets (Vendée coast, France)
Shield volcanoes are described as low-angle edifices built primarily by the accumulation of successive lava flows. This generic view of shield volcano morphology is based on a limited number of monogenetic shields from Iceland and Mexico, and a small set of large oceanic islands (Hawaii, Galápagos). Here, the morphometry of 158 monogenetic and polygenetic shield volcanoes is analyzed quantitatively from 90-meter resolution SRTM DEMs using the MORVOLC algorithm.
B. Le Mauff, M. Juigner, M. Robin, P. Launeau, P. Fattal
Geomorphology, volume 304

Multi-Satellite Altimeter Validation along the French Atlantic Coast in the Southern Bay of Biscay from ERS-2 to SARAL
Monitoring changes in coastal sea levels is necessary given the impacts of climate change. Information on the sea level and its changes are important parameters in connection to climate change processes. In this study, radar altimetry data from successive satellite missions, European Remote Sensing-2 (ERS-2), Jason-1, Envisat, Jason-2, and Satellite with ARgos and ALtiKa (SARAL), were used to measure sea surface heights (SSH). Altimetry-derived SSH was validated for the southern Bay of Biscay, using records from seven tide gauges located along the French Atlantic coast.
P. L. Vu, F. Frappart, J. Darrozes, V. Marieu, F. Blarel, G. Ramillien, P. Bonnefond, F. Birol
Remote Sensing, volume 10
![Timeline for radar altimeters used in our study (modified from [25]).](/sites/default/files/styles/large/public/2025-01/radar.png?itok=st25gSb3)
Nonlinear dynamics of the sea level time series in the eastern English Channel
Coastal flooding due to surge events represents natural hazards with huge potential consequences for coastal regions. Sea level time series display variations on a large range of timescales, with a deterministic component associated with tidal variations and a stochastic component primarily associated with meteorological forcing, the non-tidal residual. The deterministic component can be evaluated using a model taking into account astronomical forcing and topographic information.
F. G. Schmitt, A. Crapoulet, A. Hequette, Y. Huang
Natural Hazards, volume 91

Investigating the impacts of the regression of Posidonia oceanica on hydrodynamics and sediment transport in Giens Gulf
Posidonia oceanica plays a significant role in the stabilization and protection of the coast in Gulf of Giens. Unfortunately, its distribution has been declining remarkably due to both anthropogenic interventions and natural factors. The present study focuses on the numerical simulation of the presence of Posidonia as well as the influence of its disappearance on hydrodynamics and sediment transport along Alamanarre beach.
M. Tuan Vu, Y. Lacroix, V. T. Nguyen
Ocean Engineering, volume 146
